Restoring Elasticache Redis Instance You Can't Snapshot
The greatest benefit of AWS is how it easy it is. The greatest danger of AWS is how easy it is. I learned this thankfully on a small scale. Currently, I am using Elasticache redis instances in conjunction with Resque. The instance type I used to start out was t2.small. It was cheap and burstable. On the surface this seemed perfect and awesome but for some reason AWS doesn’t support snapshots for this instance type. So, of course, there came the day where I had to upgrade from Redis 2.6 to 2.8. The easiest method would be to take a snapshot and create a new replication cluster from a restored Elasticache snapshot. However, I can’t snapshot. So uh oh. What to do? Luckily using the S3 seed features you can restore it yourself.
If you don’t already download and install redis-cli. redis-cli tutorial
Create a RDB snapshot. According to the Redis docs: “RDB is a very compact single-file point-in-time representation of your Redis data”
So do this:
redis-cli -h your_elasticache_endpoint.aws.com --rdb dump.rdb
Next, upload the file to an S3 bucket. And grant open/download permissions to aws-scs-s3-readonly@amazon.com.
Now create a new cluster and seed the new cluster with your RDB file. Make sure to include S3 Location of Redis RDB file like so:
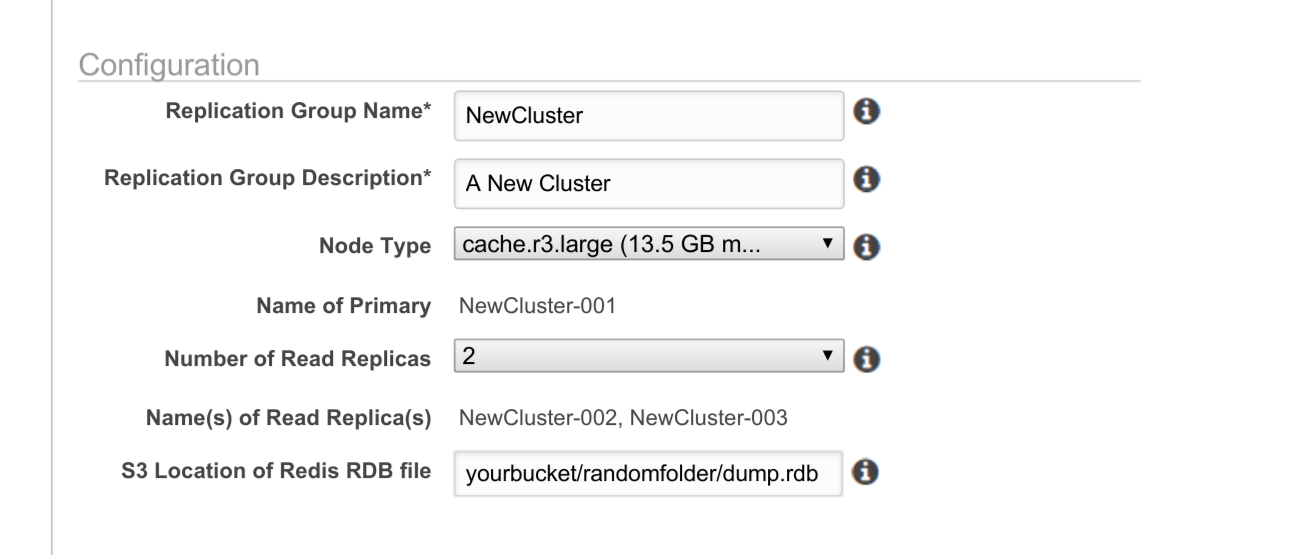
After the cluster is initialized your data should be seeded in your new cluster and you should be good to go.